4.5. Data Sources¶
To import data from reports in MQC, the data has to be provided as files. These files can be located in the local file system, a network path or a git repository.
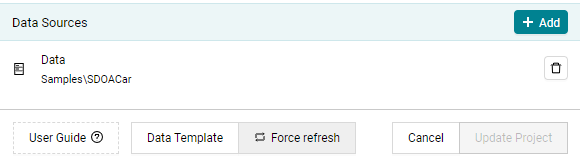
Figure 4.31 Data sources in MQC. By clicking on “Add” a new data source can be configured.¶
A new data source can be added through a browser in the data source dialog. The type of the data source has to be selected first and then the respective directory, files or git repository can be added. You can add multiple data sources to your project.
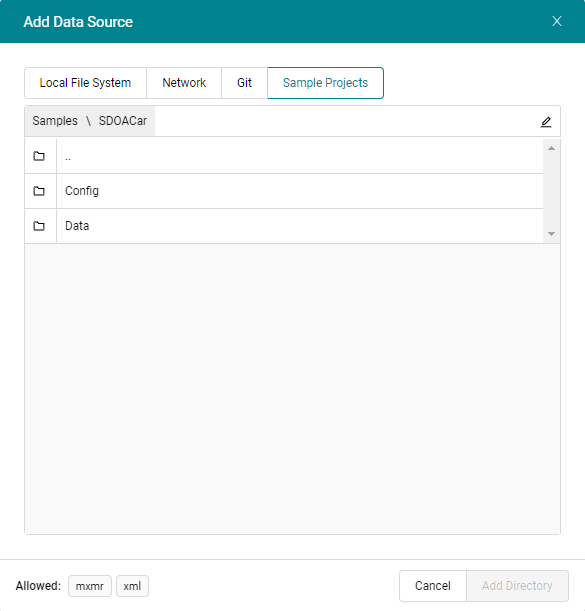
Figure 4.32 The Browser to add a new Data Source¶
Each data source is constantly monitored for updates and changes. Whenever e.g. a new report appears in a data source (new file in directory or new commit in version control system), it will be detected by MQC. Either the user is notified about the changes or the project is automatically updated.
4.5.1. Local File System / Network / Sample Projects¶
The local file system and network types function similarly. A directory, and therefore all subdirectories and files within, or a single file can be selected as the data source. At any point, the allowed file extensions that can be read by MQC are displayed below.
Navigating through the file system works like a windows explorer. Double-clicking a directory opens it. The current path is displayed at the top of the browser and can be used to navigate upwards in the file system. You can also add the path manually.
Figure 4.33 Local File System selected. Add/Edit the path manually.¶
Figure 4.34 Network selected. The path can be used to navigation upwards by click.¶
The local file system of the server is not accessible when using the web player.
You have also direct access to the MQC Showcase source files under Sample Projects
(see Figure 4.32).
4.5.2. Version Control Systems¶
MQC also allows version control systems to be used as a data source. Currently only Git is supported.
4.5.2.1. Git¶
After selecting Git as data source type, a Git repository URL can be added.
In case you have multiple repositories with a similar structure, you can
configure them as one data source. Use the Add Repository button to
extend the list of repository URLs or paste a list of repositories to the
edit field, which automatically leads to multiple lines
(see Figure 4.35).
Each repository is checked then for availability and accessibility separately. If an authentication is required, you will be asked for your credentials.
If git is not installed, locally (if using the MQC desktop client) or on the server (if using the web player), an error is shown.
Git for windows can be found here: https://git-scm.com/downloads
Git repositories can be added by ssh or https urls.
An rsa private key can be provided for authentication of ssh urls if it is not configured as the default ssh key for the current user.
For an https url the authentication has to be done by entering the username and password, if it is not already stored in the windows credential store.
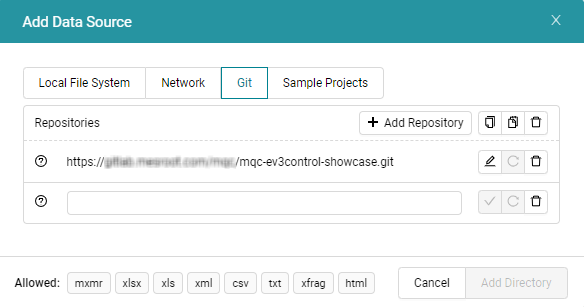
Figure 4.35 Git Repositories dialog to add, edit and remove git repository(ies) to be configured as one data source.¶
If the configured repository(ies) contain multiple branches, you can select a branch via the drop down next to the list of repository URLs.
Only branches that exist in all repositories can be selected, when multiple Git repositories are given.
Since your commit history might contain commits not relevant for your MQC quality analysis, you have the possibility of filtering these commits in the Commit Filters section of this dialog (see Figure 4.36).
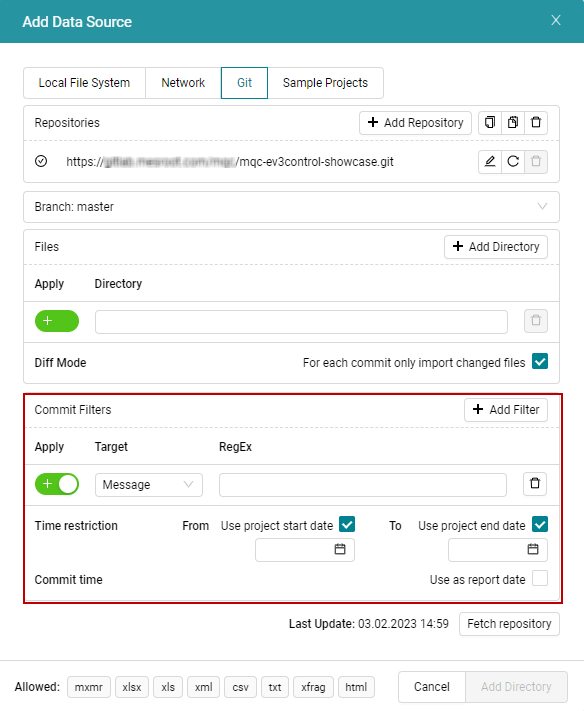
Figure 4.36 Configuration options to add a commit filter.¶
The Commit Filters section provides three possible targets to filter, namely,
Message, Author and Tag. You can further choose to either include
or exclude the commits matching this filter by clicking on the toggle button
below Apply. The green colored + stands for include and the red colored
- stands for exclude. Define a suitable regular expression in the RegEx
text box. All the filters to the same target are connected with an OR
whereas different targets are connected with an AND.
Figure 4.37 shows a filter that matches all commits
From the Author "Jenkins Slave" AND with (Message "Static
Analysis" OR Message "Dynamic Analysis").
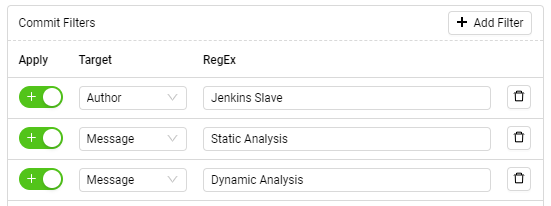
Figure 4.37 Commit Filters with “AND” between different targets and “OR” between the same targets.¶
Additionally, MQC offers the possibility to filter by time (see Figure 4.36). This allows to consider only commits of a specific time frame. First and last commit time can be configured separately by:
using the start and end date of the project (as defined by the milestones within a project structure configuration, which is also the default if nothing is set at all)
selecting a specific date via the date picker.
If no project structure configuration has been added, all commits are fetched from the repository(ies).
If a commit appears outside the configured project time frame, you will be notified about such commits within the Notifications panel. After adapting the project structure configuration, a data refresh is necessary to fetch the relevant commits from the repository.
With the checkbox shown in Figure 4.38 you can define which date and time is used as the report date-time:
Git commit date (checked)
Report creation date time as contained in the report itself (unchecked)
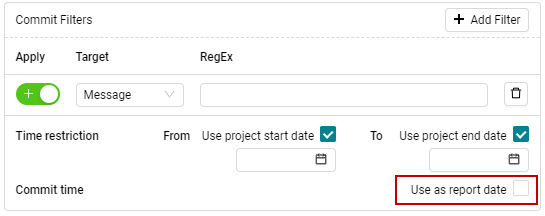
Figure 4.38 Enable checkbox to use commit time as report date.¶
In addition to the commit filters, it is also possible to select specific folders or files relevant to your analysis. MQC provides two possibilities to do this.
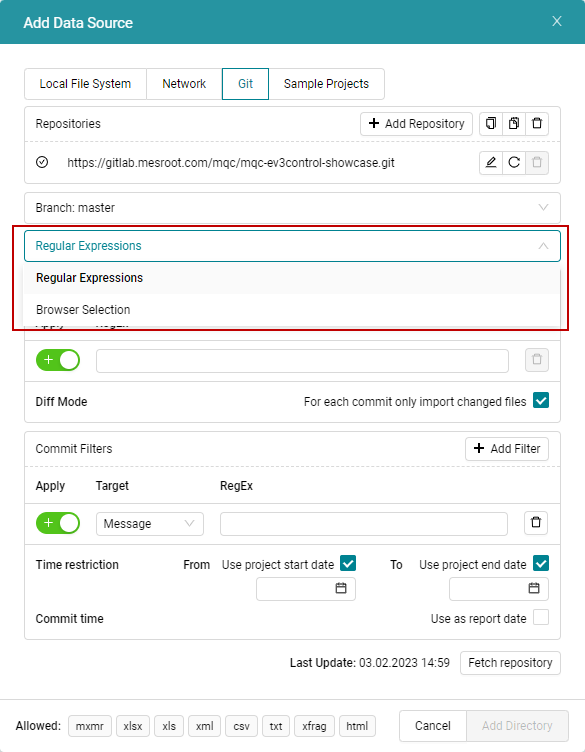
Figure 4.39 Selection menu to choose the folder or file path of relevant data by file system or add patterns to match relevant folder or file paths.¶
If you select the Regular Expressions option in
the drop down, then you can add multiple regular expressions similar to the
Commit Filters section.
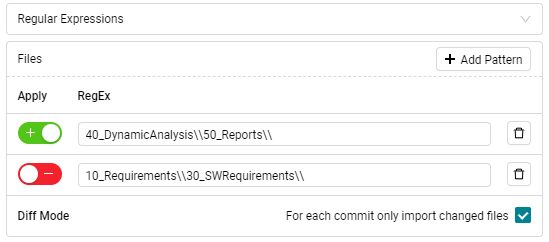
Figure 4.40 Regular Expression pattern matching for selecting data source paths.¶
If you select Browser Selection option, one file or folder can be chosen
as the data source, similar to selecting directories from a local or a network
drive as data source.
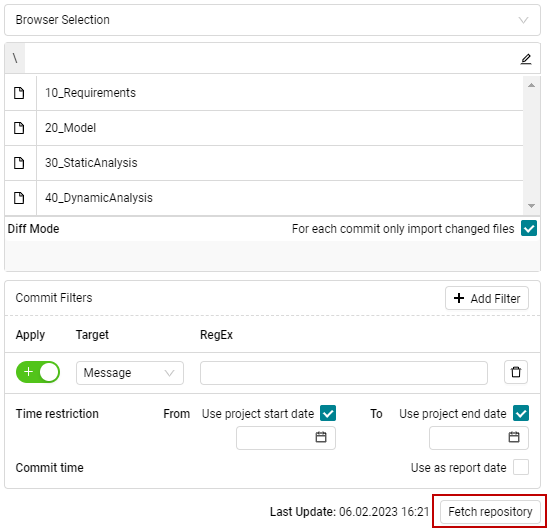
Figure 4.41 Browser Selection for choosing data source path.¶
The Browser Selection is only available when using a single Git repository
as data source. For multiple repositories only Regular Expressions
could be applied. Additionally, to be able to navigate within and to select
specific folders, it is necessary to fetch the repository first by using the
Fetch repository button in the left-right corner
(see Figure 4.41).
Since the version 6.3, MQC supports the partial checkout feature (sparse checkout) provided by Git. Using sparse checkout, no full clone of the git repository is performed. Only the relevant files and directories based on the defined filters are downloaded from the server.
Using the sparse checkout has to be enabled by an administrator. The corresponding configuration is described in the Server Administration Guide.
If sparse checkout is enabled, no browser selection is possible. Additionally, it is not possible to define “exclude” filters for directories as shown in Figure 4.40. Instead of regular expressions for directory paths, the names of the directories have to be used as filter.
If a git data source has been added, a monitoring service periodically checks if a new commit is made on the remote. The default for the check interval is set to 10 seconds. In case of multiple repositories, the supervision timer is stepwise increased for performance reasons based on the number of repositories. I.e. If you have configured more than 100 repositories, the check happens only every 60 seconds.
When data is refreshed, the git repository is updated and all remote changes
are fetched and applied to the MQC project. In case some hidden changes were
made in your Git repository, use the Force Refresh button (see
Figure 4.31) to not just apply changes to
a project but to re-import all data anew.