4.1. Creating an MQC project¶
There are two options, how to set up an MQC project:
4.1.1. Creating a project from scratch¶
To create a project from scratch after opening MQC, you have two options (see Figure 4.1).
Either open the dialog on the left-hand side (click on the
+in the top left corner) and chooseCreate new Project.Or use the
Create Projectoption within the section inside the main window of the MQC landing page (only available if MQC has been newly started).
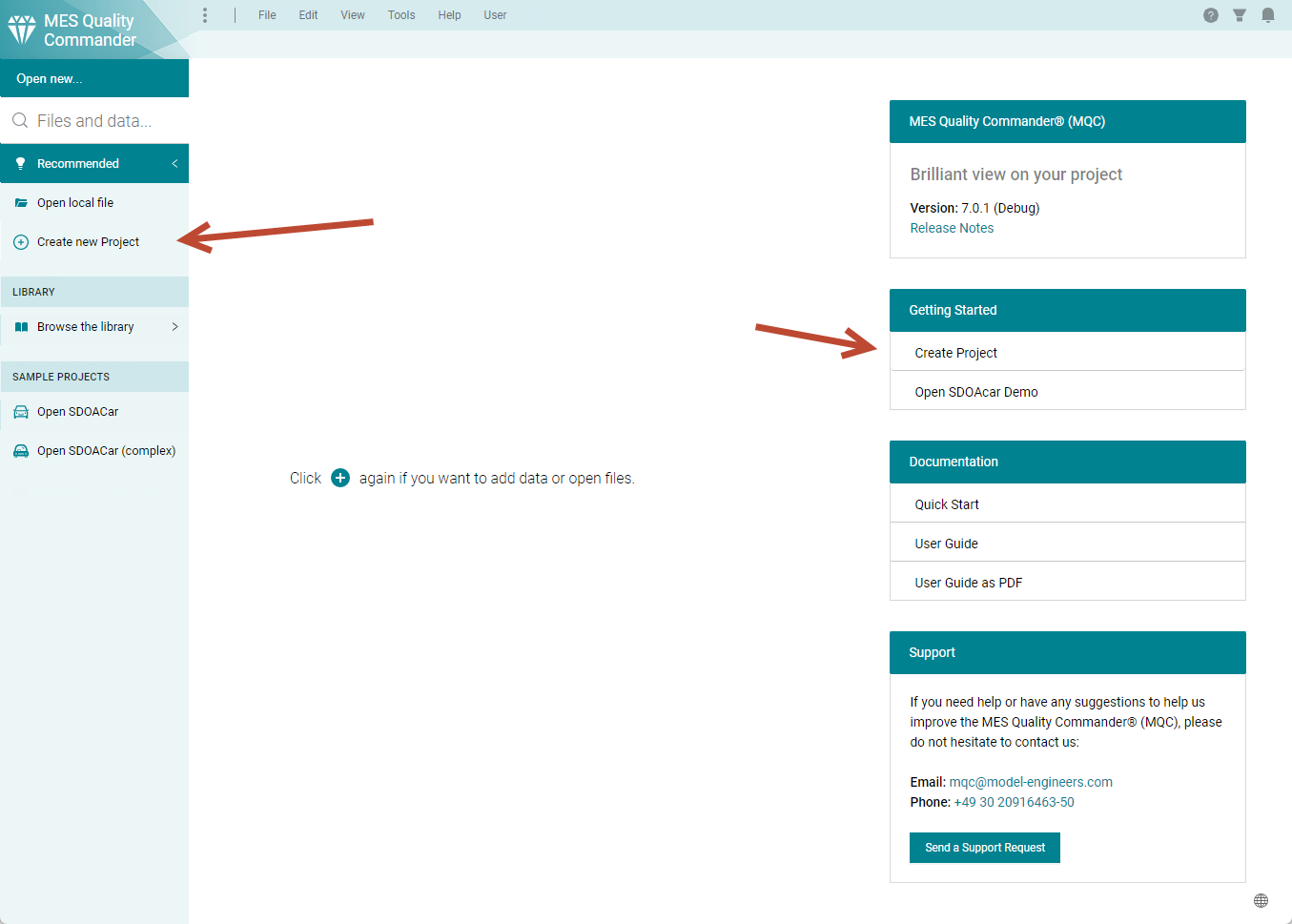
Figure 4.1 Start creating a new MQC project via the entry in the left-hand side panel or via the menu entry in the section inside the main window¶
A dialog (Figure 4.2) opens asking for the location of your data (see Data Sources) and allows to change the revision granularity used (see Revisions).
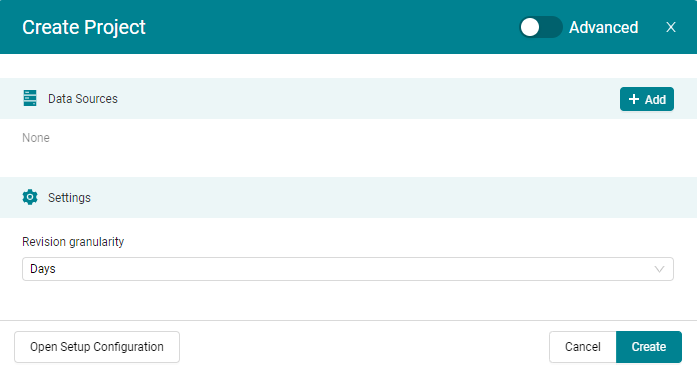
Figure 4.2 Create Project dialog (simple mode) to initially configure the data source(s) and to set the revision granularity¶
After confirming the dialog using the Create button, a new project is set
up with the data contained in your data source(s) and defaults for all
remaining settings (see Settings).
All default settings used for project creation may be changed later via the settings dialog (see Settings).
In case you would like to adapt further settings, e.g. Switch on Propagation, add a quality model configuration (see Quality Model) or project structure (see Project Structure), you can switch to the advanced mode of the Create Project dialog as shown in Figure 4.3 by using the switch in the top-right corner.
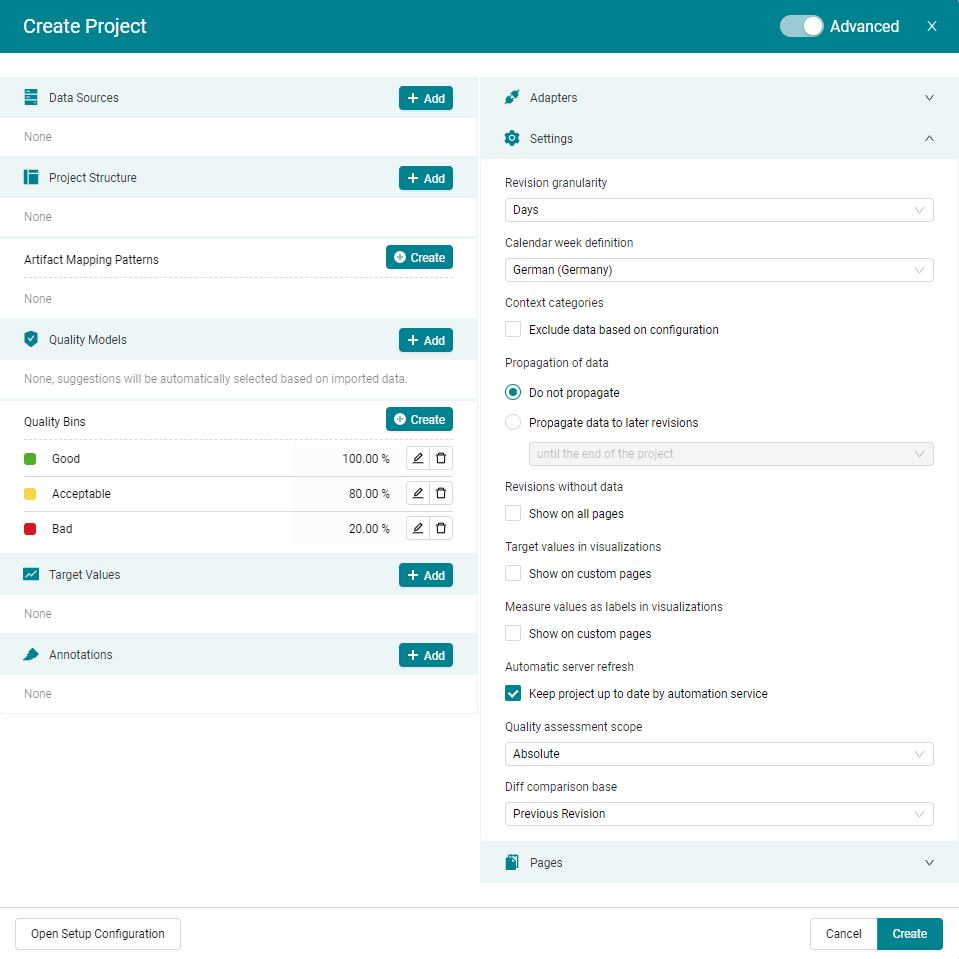
Figure 4.3 Create Project dialog (advanced mode) to import data source(s), quality model(s), project structure and to change the settings before creating a project.¶
The advanced mode of the Create Project dialog allows you to load all configuration files and to adapt all necessary Settings to be already applied during project creation. This facilitates a fast and comprehensive setup process.
In case you switch back from advanced to simple mode, nevertheless all your previously made settings will be kept and applied when creating the project.
If you confirm the dialog without selecting a data source, an empty project is created. This might be useful in case you don’t already have data for your project, but would like to do all necessary configurations in advance.
Data sources can be added at any later point in time (see Data Sources).
4.1.2. Creating a project using a Setup Configuration¶
MQC provides the possibility of importing a setup configuration (see Importing a setup configuration) to easily set up a project. This configuration can be created in two ways:
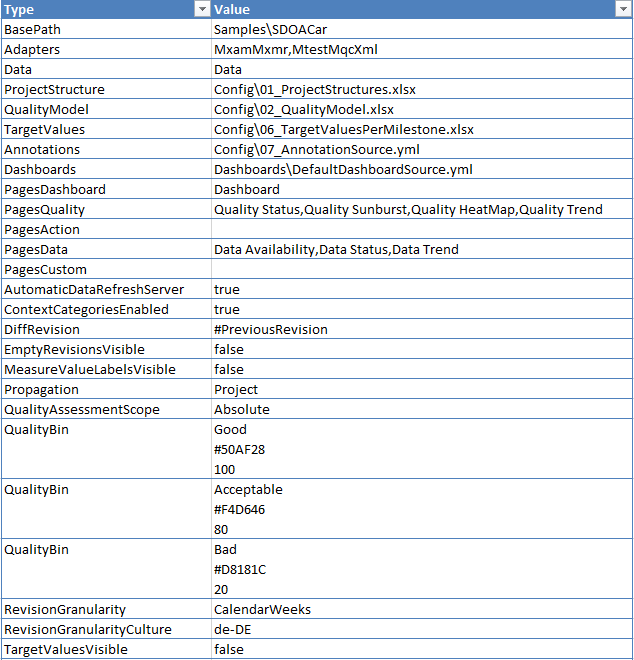
Figure 4.4 Sample of setup configuration file¶
4.1.2.1. Exporting a setup configuration from an existing project¶
In MQC you can export a setup configuration file, which contains all the settings done in the current project in order to use it as backup for a fast re-creation of the current project or to use it as a template for creating other similar projects.
Open the dialog via the configuration menu and select
the Setup Configuration button to export the current configuration as Setup
Configuration (see Figure 4.5).
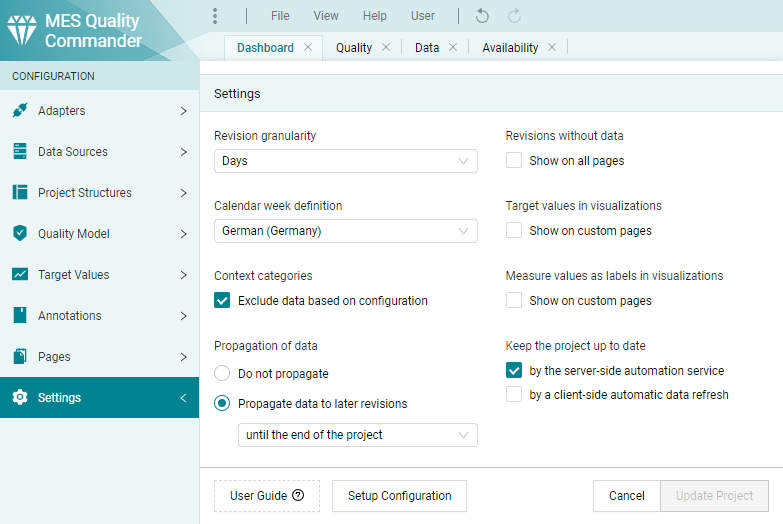
Figure 4.5 How to export Setup Configuration Excel file for current project¶
4.1.2.2. Manually configuring a setup configuration¶
For the setup configuration the user can define:
files and directories containing reports of tools/data sources to be imported into MQC
names and paths of MQC configuration files, e.g. project structure
as well as almost all options, e.g. revision granularity.
All values described in the following may be left empty. MQC applies defaults for all values, which are not configured in the setup configuration.
Errors in the configuration will be ignored. In any case a project is created and the user gets a notification via a validation dialog after the load of the setup configuration has been finished.
As shown in Figure 4.4, each configuration entry
consists of a Type, which is fix, and a Value, which can be configured.
This configuration can be divided into three parts:
Set the paths of all files that can be imported in MQC. This contains:
(optional): The first row can be optionally used to set a base path. If all files (reports as well as configuration sources) are located under the same path, this can be defined once as and all other path values may be configured as relative paths.
: Data sources containing reports of tools. For each data source one row is added to the setup configuration.
Files and directories: The path of them has to be used as value.
Git Repository(ies): Provide the URL for the git repository to be used as a data source. Multiple repositories can be added as one data source (one row), if the same commit filter and file pattern configuration applies. The respective filter configurations are added as additional lines in the same cell (see Git).
: Path of configuration source file (see Project Structure).
: Path of configuration source file (see Quality Model).
: Path of configuration source file (see Target Values).
: Path of configuration source file (see Annotations).
: Path of configuration source file (see Dashboards).
: Path of configuration source file (see Custom Pages).
: For each custom adapter, a separate row should be added and the path of the source file has to be given as value (for more detailed information please see Developing a Custom Adapter).
In case of multiple configuration source files of the same type, e.g. if multiple Quality Models have to be imported, for each configuration source file a separate row has to be used.
Set default values for MQC options. This contains:
: List of base adapters which should be enabled in MQC, all entries are separated by . If empty or not defined, all base adapters are enabled. For more detailed information please see Adapters.
: There should be one Excel row for each pattern (see Artifact Mapping Patterns). The value cell contains two lines: the first line is the Search RegEx and the second line is the corresponding Replace.
: Can be true or false (see Keep the project up to date).
: Can be true or false (see Context Categories).
: The comparison base to be used for Diff pages and visualizations. Use one of the following options:
“#PreviousRevision”
“#PreviousMilestone”.
: Can be true or false (see Revisions without data).
: Can be true or false (see Measure values as labels in visualizations (Custom pages)).
: Can be “None”, “Project” or “Milestone” (see Propagation of data).
: The scope of quality assessment. Use one of the following options:
“Absolute”
“Available”
“Relative” (only if target values are defined).
: For each quality bin, a separate row should be added. Name, Hex Color Code and Upper Quality Boundary have to be added each on new line as value (see Quality Bins).
: Can be “Months”, “CalendarWeeks” or “Days” (see Revision granularity).
: The calendar week definition (see Calendar week definition).
: Can be true or false (see Target values in visualizations (Custom pages)).
3. Set the pages, which should be shown in the analysis. For each row from a group of provided pages in MQC (page type), the chosen pages should be added and separated by . Supported page types are:
For more detailed information please see Pages.
4.1.2.3. Importing a setup configuration¶
As shown in Figure 4.6, click on Open local file
within the dialog on the left hand side to
import a setup configuration file.
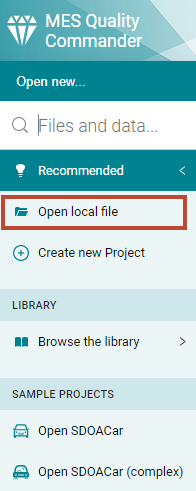
Figure 4.6 Import a Setup Configuration Excel file for easy setup of MQC¶
Then navigate to the folder where you have stored a previously created setup configuration file, select the file and confirm the dialog.
Alternatively, you may use the Open Setup Configuration button in the
dialog to import a setup configuration file
(see Figure 4.7).
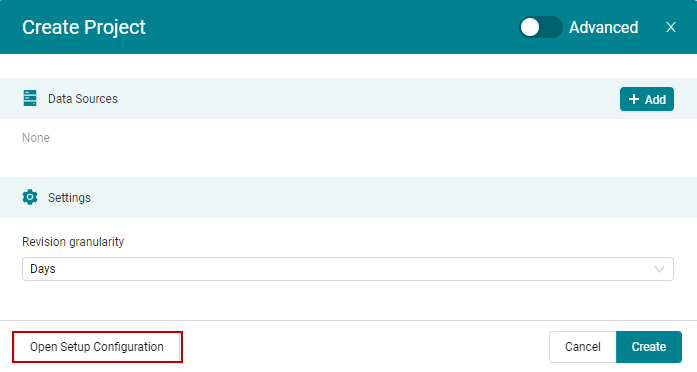
Figure 4.7 Import a Setup Configuration via the dialog¶
In both cases, the setup configuration settings are used to pre-fill the dialog. This offers the possibility to check and potentially adapt the whole configuration before finally creating the project. Any misconfiguration is notified and is replaced by defaults.
If you are using the web version of MQC, before importing a setup configuration you need to ensure that the setup configuration file is located on a network drive, which is mounted at and can be accessed by the server. The value within the configuration file should be set to the network path of the directory where your project data is located.