25. Setup Configuration¶
MQC provides the possibility of loading a setup configuration to easily setup a project. This is done via an Excel file in which the user can define
files and directories containing reports of tools/data sources to be imported into MQC
names and paths of MQC configuration files, e.g. project structure
as well as almost all options, e.g. revision granularity.
25.1. How to use¶
After unziping sample data you can find an example for an setup configuration in it with the name of , configured for MQC showcase.
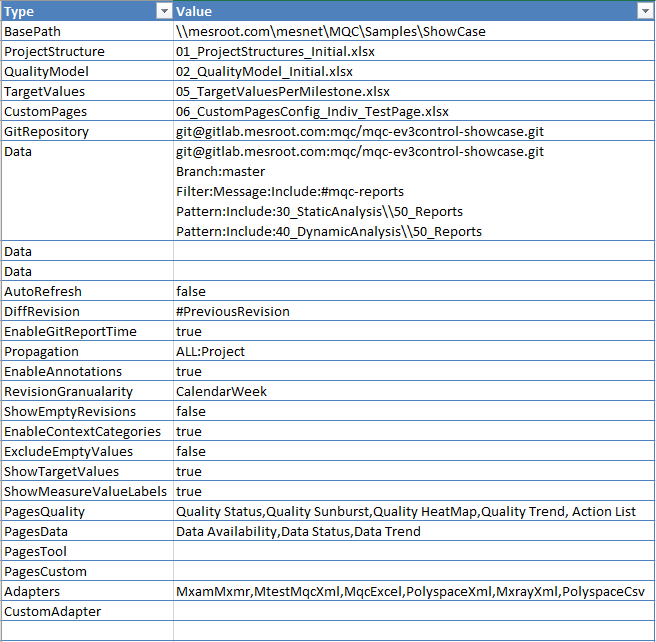
Figure 25.1 Sample of setup configuration file¶
For using this feature, first copy sample data anywhere in your local file
system or network, then open MQC and instead of choosing
, import
by clicking on
Open local file....
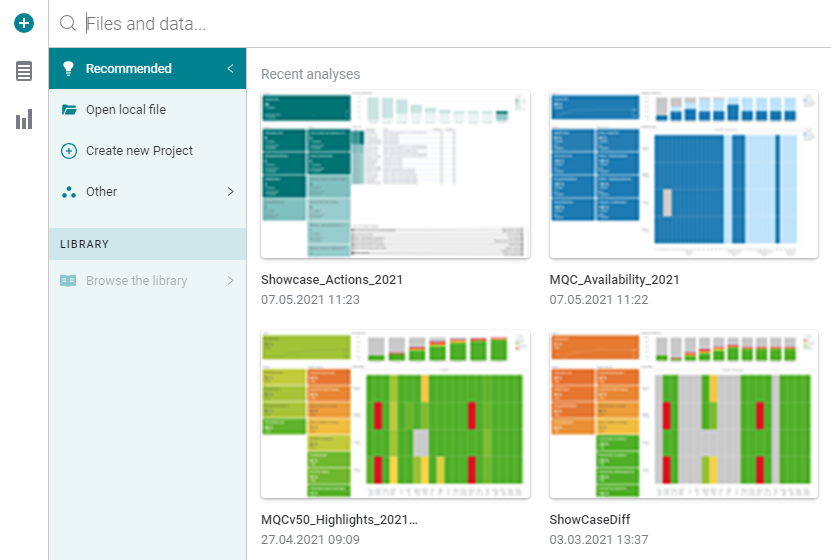
Figure 25.2 How to import Setup Configuration excel file for easy setup of MQC¶
Note
If you are using the web version of MQC, before importing a setup configuration you need to ensure that the MQC showcase is located on a network drive, which is mounted at and can be accessed by the server. Open the and update the value with the network path of the directory where the MQC showcase is located.
25.2. Configuration¶
The setup configuration is an excel file with two columns named Type and
Value. Contents of first column (Type) are constant and second column
should be configured.
This configuration can be divided in three parts:
Set the paths of all files that can be imported in MQC. This contains:
Project structure configuration (see Project Structures Configuration)
Quality model configuration (see Quality Model Configuration)
FML file selection: If action derivation needs to be done using fuzzy rules, then the file path for the FML file must be added here (see Actions)
Target values configuration (see Target Values)
Custom pages configuration (see Custom Pages)
Git Repository configuration: Provide the url for the git repository to be used as a data source. For each repository to be configured, one row is added with type
GitRepositoryand the url as value.Git data source configuration: For each git data source a new row must be added with type
Dataand the respective configurations separated by a new line as value. The first line must consist the url of the git repository. Next, the name of the branch of this repository to be used. This can be followed by multiple commit filters and file patterns required to narrow down the selection of files to be imported from this data source (see Figure 25.1 resp. Git (Beta)).Files and directories containing reports of tools/data sources: for each of directories and single files to be imported, one row is added to the setup configuration file via type
Dataand path of them as value.Custom adapters: for each custom adapter, a separate row should be added with
CustomAdapteras type and path of file as value. For more detailed information please see Developing a Custom Adapter.
Note
As Figure 25.1 shows, the first row of the setup configuration is for setting a . If all files are located under the same path, this can be defined one time as and all other path values may be configured as relative paths.
Set default values for MQC options. This contains:
Automatic refresh: can be true or false (see Refresh Data)
Propagation: can be None, All:Project or All:Milestone (see Data Propagation)
Revision granualarity: can be Month, CalendarWeek or Day (see Revision granularity)
Diff Revision: The comparison base to be used while calculating difference for Diff pages and visualizations. In case of a relative comparison base the selection type must be prefixed with a # and written in camel case, for example, “#PreviousRevision”. In case of fixed comparison base the revision name must be added directly as value (see Quality Diff and Availability Diff).
Git Report Date Time: can be true or false (see Report date & time)
Show empty revisions: can be true or false (see Project Milestone Structure).
Enable context categories: can be true or false (see Configuration of Context Categories)
Enable annotations: can be true or false (see :ref: annotations)
Show target values: can be true or false (see Target Values)
Show measure value labels: can be true or false (see Adapt Visualizations on Custom Pages)
Adapters: list of base adapters which should be enabled in MQC, all entries are separated by , if empty or not defined all base adapters are enabled. For more detailed information please see Custom Adapters.
ArtifactMappingPattern: there should be one excel row for each pattern (see Artifact Mapping) and in Value cell first line is Search RegEx and second line is Replace.
3. Set the pages, which should be shown in the analysis. For each row from a group of provided pages in MQC, chosen pages should be added and separated by . For more detailed information please see Manage Pages
Note
All values may be left empty. MQC applies defaults for all values, which are not configured here.
Errors in configuration will be ignored. In any case an analysis is created and the user gets a notification via a validation dialog after the load of the intial configuration has been finished.
25.3. Export Setup Configuration¶
In MQC you can export a setup configuration file, which contains all the
settings done in the current project in order to use it for creating other
projects. For that please choose the Export Setup Configuration button in
section of configuration menu.
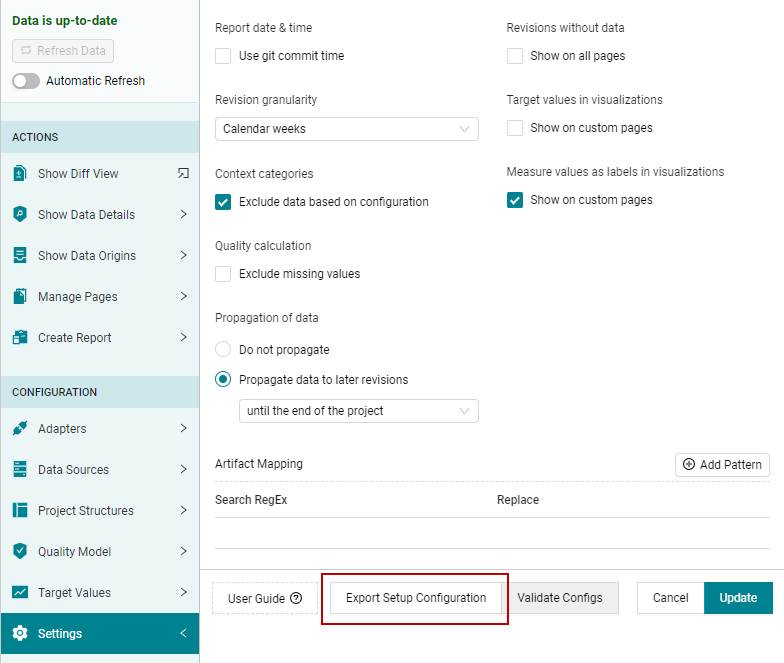
Figure 25.3 How to export Setup Configuration excel file for current project¶