19. Annotation Configuration¶
MQC provides the possibility to annotate the quality of the quality properties and artifacts in your project. This functionality allows you to add a description to justify the observed quality for a duration of your project. This description/comment allows other users to know why a certain quality property might be performing poorly. In this way the justification is documented in a more transparent way.
MQC objectively calculates the quality of your project. This can be configured in Quality Model, Project Structure, Target Values, and Context Categories, etc.
For special, real-world cases you could use annotations to document deviations from expected values. Additionally, you can use annotations to change the quality value or bin if they need to be treated differently than the one calculated.
See When not to use Annotations to learn about use cases that have to be treated by other MQC features rather than using annotations.
Use annotations sparingly to describe or justify the quality of certain quality properties and artifacts. Modify the quality value or bin only if necessary.
19.1. Create and Edit Annotations¶
To configure annotations go to the Actions and Configuration menu on the left-hand side and select Annotations. This opens the Annotations dialog.
To create a new annotation select Create at the top right of the
dialog.
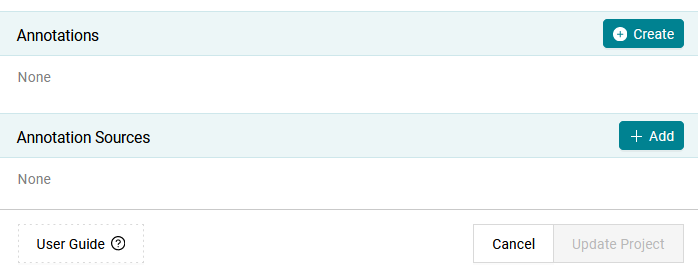
Figure 19.1 Create a new annotation by clicking on the Create button.¶
This opens a form that has to be filled out by the user.
Note
If you had already marked certain artifacts, quality properties from the
KPIs or an element from the main visualization, the marked elements are
pre-selected respectively in the Annotations dialog as well as in the
Create Annotation dialog. If you would like to remove this pre-selection
simply uncheck the Show marked only check box at the top of the
Annotations dialog.
If an element was marked in the main visualization, the
Valid From, Valid To and Bin fields will also be filled automatically
with the corresponding information.
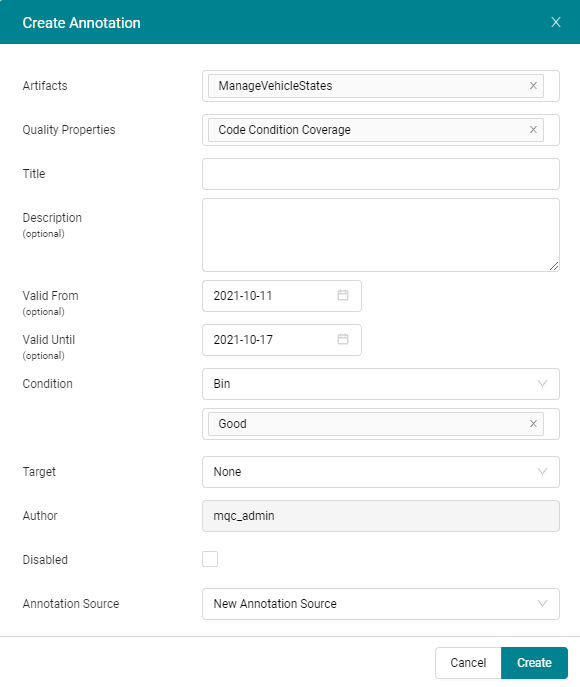
Figure 19.2 Prefilled form to create an annotation after selecting a quality tile in the Quality Status matrix.¶
When no quality properties or artifacts were selected, the form is empty and has to be filled out completely.
The following fields are available to define an annotation.
Artifacts: (mandatory) Select one or more artifacts this annotation should be applied to. The drop-down menu restricts you to the artifacts present in your project.
Quality Properties: (mandatory) Select one or more quality properties this annotation should be applied to. The drop-down menu restricts you to the quality properties defined in the quality model.
Title: (mandatory) Add a caption or a title to identify the annotation easily or to provide a quick overview of the annotation.
Long Description: (optional) Here you can add a more detailed justification or description of the annotation.
Valid From: (optional) Select the start date in the calendar from which the annotation is active. If left empty MQC treats the annotation as active from the start date of the project.
Valid To: (optional) Select the end date until which the annotation is active. If left empty MQC treats the annotation as active until the end date of the project.
Condition: Define the qualifying condition based on which the underlying quality value or bin would be changed. The first drop-down menu allows you to select the type of condition. By default the condition is set to
Bin. The field below selects the bins defined in your project for which the annotation must be active. If you selectQualityas the condition type you will see a range selection bar. Here you can select the range of quality for which the annotation must be active.Target: Define the target quality value or bin you would like to annotate when the condition defined above is true. By default the target type is set to
Binand you can select only one target quality bin. If you selectQualityin the drop-down menu you can change the target quality value with the slider or edit the field directly.Disabled: Enable or disable an annotation. Disabled annotations are not applied but remain in the project and can be enabled at any point in time.
Annotation Source: (mandatory) Assign the annotation to annotation source. By default a New Annotation Source with the name NewAnnotationSource.yml will be added and the annotation will be stored in this source. Later NewAnnotationSource.yml can be saved (see Save and Export Annotation Sources).
You can use different combinations of qualifying conditions and desired target values for an annotation. For example:
If you want to change a quality bin from Bad to Acceptable, set the Condition type to Bin and select the quality bin
Bad. Then set the Target type to Bin and select the quality binAcceptable.If a quality bin is too broad you could use the Quality condition instead. Set the Condition type to Quality and select a range between
10to15. Then set the Target type to Bin and select the quality binAcceptable.If the target bin makes the quality too high and you would like to specify it directly, then set the Target type to Quality and the quality value to
25.Finally, you can also define the condition as bin and target as value. Set the Condition type to Bin and select the quality bin
Bad. Then set the Target type to Quality and the quality value to25.
Note
If the target is a bin then the underlying quality value is also changed and vice versa. The respective values are chosen from the bin configuration defined in the quality model (see Quality Model and Quality Bin Configuration).
Once annotations are created, they can be seen in the Annotation dialog.
If any field is invalid it is marked in red, the annotation is grayed out,
and the annotation cannot be applied to the project, for example, if the
Valid From or Valid To dates are outside the timeline of the project.
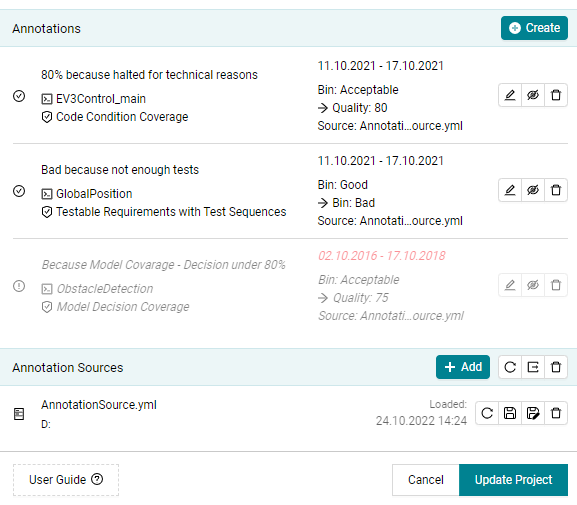
Figure 19.3 Annotation dialog after annotation is created.¶
Each annotation can be edited in the Edit Annotation dialog which is the same
as the Add Annotation (Figure 19.2).
Select Update to save the changes.
If you have made any changes, that is, added, edited, enabled, disabled or
deleted annotations, select Update Project to apply these changes to your
project. All the changes will then be visible. If you don’t apply these changes
and try to close the Annotations dialog, another dialog will pop out (Figure 19.4)
informing that the changes should be saved (Update Project) or discarded (Discard).
By pressing Back you go back to Annotations dialog.
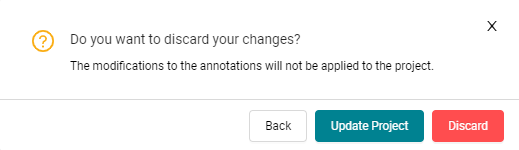
Figure 19.4 Cancel warning dialog.¶
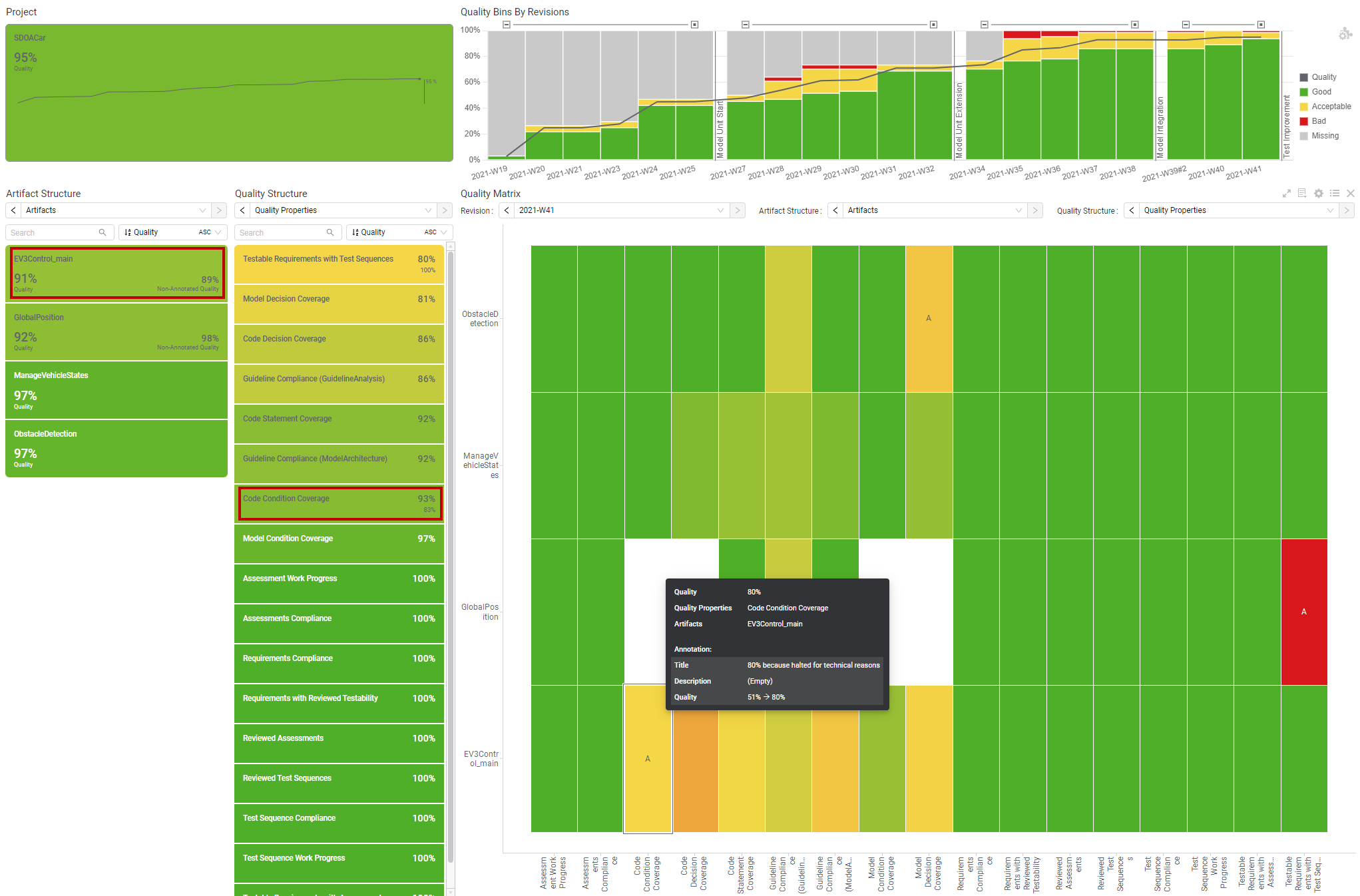
Figure 19.5 Quality status page with annotations applied to your project.
Non-Annotated Quality stands for the quality value before annotation
was applied.¶
MQC displays applied annotations:
as an “A”-Indicator inside the quality matrix (cells with annotated quality show an “A” in addition)
as an “A”-Indicator inside the Heatmap (cells with annotated quality show an “A” in addition)
within the Tooltip for an annotated quality point (title, description and the change of quality, if defined, will be displayed)
in the KPIs (the KPI value shows the annotated quality, the comparative value shows the “Non-Annotated Quality”).
19.2. Import Annotation Source¶
MQC provides the possibility to add annotation source(s) to your project by clicking
Add in Annotation dialog.

Figure 19.6 Add Annotation Source¶
To configure an Annotation source you need to create yaml file with Authors and Annotations. For each Annotation Title, Artifact, Quality Property fields are mandatory. All other configurations are optional and can be added later directly in MQC. Example of Annotation source is shown below (Listing 19.1).
$schema: http://quality-commander.de/userguide/v61/schema/AnnotationSource.schema.json
$version: 1.0
Authors:
- Model Engineering Solutions GmbH
Annotations:
- Title: '80% because halted for technical reasons'
Author: mqc_admin
Artifact: EV3Control_main
QualityProperty: Code Condition Coverage
ValidFrom: 2021-10-11
ValidTo: 2021-10-17
ConditionType: Bin
ConditionBins:
- Acceptable
TargetType: Quality
TargetValue: 80.00
- Title: Bad because not enough tests
Author: mqc_admin
Artifact: GlobalPosition
QualityProperty: Testable Requirements with Test Sequences
ValidFrom: 2021-10-11
ValidTo: 2021-10-17
ConditionType: Bin
ConditionBins:
- Good
TargetType: Bin
TargetValue: Bad
- Title: Because Model Covarage - Decision under 80%
Description: see Data Origins
Author: mqc_admin
Artifact: ObstacleDetection
QualityProperty: Model Decision Coverage
ValidFrom: 2021-10-11
ValidTo: 2021-10-17
ConditionType: Bin
ConditionBins:
- Acceptable
TargetType: Quality
TargetValue: 75.00
In this way an annotation file may be used for multiple projects as well.
Note
The possibility to add annotation source(s) allows you to import annotations that are not fitting to your project. These annotations are considered unmatched and are displayed as shown in Figure 19.3. After loading, you can edit these unmatched annotations to make them applicable to your current project.
19.3. Save and Export Annotation Sources¶
Once created some annotations within the tool, they are kept in Unsaved Annotations.
You can save this annotation source using Save As and selecting name and
destination for the source file.
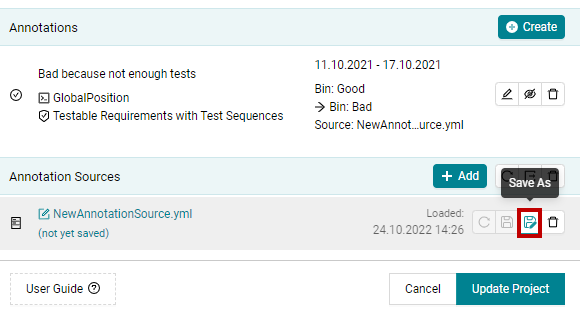
Figure 19.7 Save As button to save annotation source.¶
Once you have saved your annotation source or loaded annotation source, MQC keeps a file reference. By that it is possible to simply reload if the content of the file has been changed outside MQC.
If you have done some changes to the annotations in MQC through Edit Annotation Dialog,
MQC indicates that the corresponding annotation source has been changed as shown in
Figure 19.8. Then using Save you can save all the changes to the
initially loaded file.
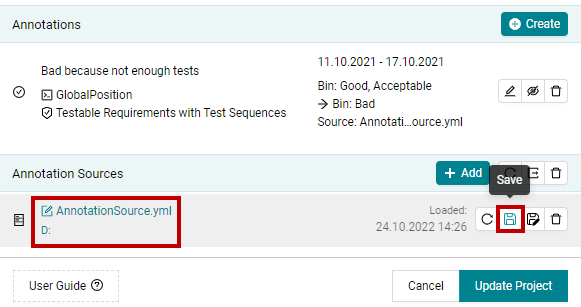
Figure 19.8 Save button to save all changes.¶
Note
The possibility to Save As annotation sources is always
active and after that the new file reference is kept in MQC.
If you have multiple Annotation sources configured you can export all annotations or annotations
from multiple sources in one source through the Export button. It is also possible
to reload or delete each Annotation source individually. Furthermore, MQC allows to
reload and delete all source files at once.
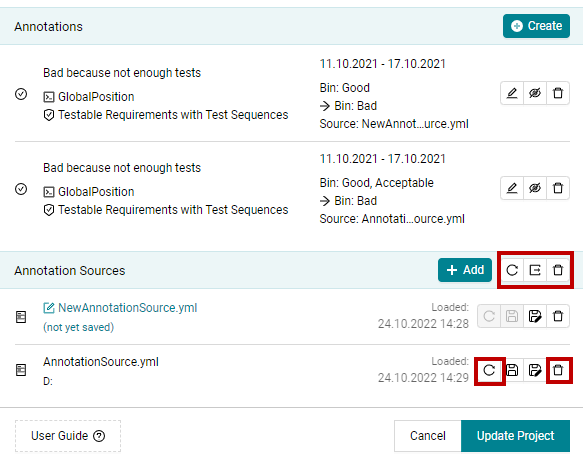
Figure 19.9
Reload,Export,Deleteall buttons andReloadandDeleteindividually.¶
19.4. When not to use Annotations¶
Annotations should be used to justify very specific and local deviations, especially if such a deviation applies to a specific point in time only. Particularly, annotations should not be used to cover one of the following cases.
If you don’t expect any data measure and don’t want MQC to calculate quality for a particular artifact respectively model, this artifact should be excluded from the project using a proper Project Structure configuration (see Artifact Structure).
If you don’t want to track a certain quality for a particular artifact, you should use context categories to exclude the underlying data for that particular artifact (see Context Categories). If data is excluded for an artifact, also the quality resulting out of this data will not be calculated for that artifact.
If the measured data values, that are loaded into MQC, objectively imply a certain quality, but the resulting quality value shown in MQC does not reflect that, the corresponding quality measurement function should be adapted accordingly (see Quality Properties).
Define targets for quality values (see Target Values) rather than using annotations as justification. By using targets, you may specify that the relative quality is 100% if the configured target was reached or even exceeded, even if the calculated absolute quality does not reflect that at all, but meets the expectations for that point in time.